- Plot No. 361/3074 & Plot No 437/3134, Patrapada, BBSR
- +91 9040017001
- +91 8630400500
Kidney Cancer: Everything You Should Know
Kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in our lower back. They clean our blood, remove waste, and balance body fluids. Like other organs, kidneys can also develop cancer. Understanding kidney cancer and spotting its signs early can save lives. Let’s explore everything you need to know about kidney cancer in a simple and clear way.
What Is Kidney Cancer?
Kidney cancer happens when the cells in your kidney grow abnormally and form a lump (tumor). These cancerous cells can spread to other parts of the body if not treated on time. The most common type of kidney cancer in adults is renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
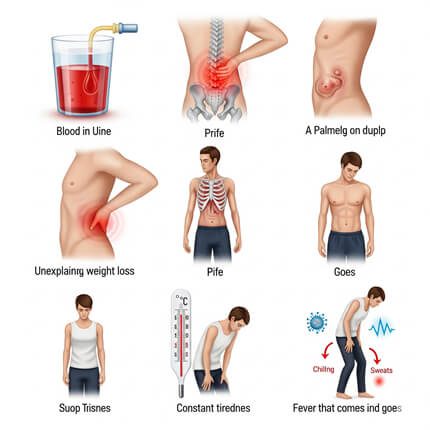
Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
In the early stages, kidney cancer often has no symptoms, which is why regular health checkups are important. However, as the disease grows, you might notice:
- Blood in the urine (even once)
- Pain in the lower back or side that doesn’t go away
- A lump or mass in the side or lower back
- Unexplained weight loss
- Constant tiredness or fatigue
- Fever that comes and goes without a reason
If you notice any of these signs, don’t ignore them. See a doctor for proper evaluation.
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Kidney Cancer
Doctors aren’t always sure why kidney cancer happens, but certain risk factors increase your chances:
- Smoking: Smokers are more likely to get kidney cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts more pressure on kidneys.
- High blood pressure (BP)
- Family history of kidney cancer
- Long-term dialysis
- Exposure to certain chemicals in factories or workplaces
You can reduce your risk by leading a healthy lifestyle and managing these conditions.

Who Is at Higher Risk?
Some people are more likely to develop kidney cancer, such as:
- Men (they’re twice as likely as women)
- People aged 50 and above
- Those with a family history
- Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes, BP, or obesity
Knowing your risk can help you stay alert and catch the disease early.

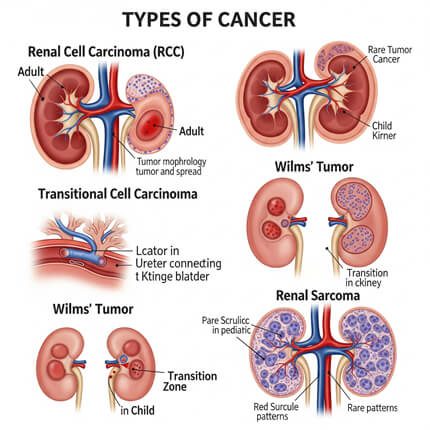
Types of Kidney Cancer
There are a few types of kidney cancer, including:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) – most common in adults.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma – affects the area where kidney connects to the bladder.
- Wilms’ Tumor – mostly found in children.
- Renal Sarcoma – rare but aggressive.
How Is Kidney Cancer Diagnosed?
If a doctor suspects kidney cancer, they may recommend:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests – to check how well your kidneys are working.
- Urine tests – to detect blood or abnormal substances.
- Imaging tests – such as Ultrasound, CT Scan, or MRI.
- Biopsy – a small tissue sample from the kidney may be tested.
Early diagnosis helps in better treatment and recovery.
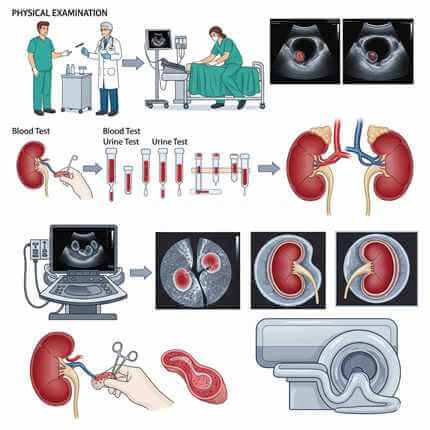
How Ultrasound and CT Scans Help Detect Kidney Cancer
- Ultrasound is a safe and quick scan that uses sound waves to create images of the kidney. It can detect if there’s a lump or abnormal mass.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography) gives detailed images and helps understand the size, location, and spread of the tumor.
These scans are painless and very important for early detection.
Why Early Detection Is So Important
Many people don’t realize they have kidney cancer until it becomes serious. If diagnosed early, kidney cancer can often be treated successfully with surgery, targeted therapy, or other treatments. Regular health checkups, especially after age 40, are crucial.
Final Thoughts
Kidney cancer may sound scary, but the good news is that early detection saves lives. Stay alert to your body’s signals, go for regular checkups, and don’t delay if you notice any symptoms. Always consult a qualified doctor for the right advice.
At Prolife Diagnostics Centre in Bhubaneswar, we offer advanced imaging like Ultrasound, CT Scans & MRI along with Image guided FNAC & Biopsy to help in early diagnosis. Your health is your wealth — take care of it today for a healthier tomorrow.
Most Viewed Posts on This Blog
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Brain Tumors: Signs, Risks & How They’re Diagnosed – A Guide for Every Family
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Top 5 Cancer Screenings Every Woman Should Know About
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Men’s Guide to Cancer Screening After 40: What to Expect
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Understanding Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Patient’s Guide
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Understanding Hemophilia: A Rare Yet Serious Bleeding Disorder
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Cervical Cancer Screening: Importance of Pap Smear and HPV Tests
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Common Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore: When to Get Tested
👨🏻⚕️ 👉 Genetic Testing for Cancer Risk: Is It Right for You?
